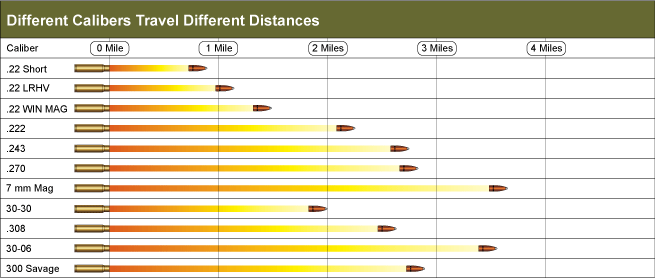
Psychology Degree Classification: Between Art and Science
The dual nature of psychology: art or science?
Psychology occupy a unique position in academia, straddle the boundaries between arts and sciences. This interdisciplinary field explore human behavior and mental processes through both humanistic and scientific lenses. Whether psychology is an art or a science have significant implications for students consider a psychology degree, peculiarly when decide between a bachelor of arts (BA) or a bachelor of science (BS) program.
Historical evolution of psychology
Psychology’s roots trace spine to philosophy, where thinkers ponder questions about human consciousness, perception, and behavior. Wilhelm Wundt establish the first psychology laboratory in 1879, mark a pivotal shift toward scientific methodology. This historical transition represents the field’s evolution from philosophical inquiry to empirical investigation.
Throughout the 20th century, psychology continue to develop along both humanistic and scientific paths. Freudian psychoanalysis emphasize interpretation and narrative understanding, while behaviorism champion rigorous experimental methods. This dual development reflects psychology’s ongoing position at the intersection of arts and sciences.
The scientific elements of psychology
Empirical research methods
Modern psychology rely intemperately on scientific methodology. Psychologists design control experiments, collect quantitative data, and apply statistical analyses to test hypotheses about human behavior. Research in cognitive psychology, neuroscience, and experimental psychology adheres to the scientific method with its emphasis on objectivity, replicability, and falsifiability.
Neuropsychology and physiological psychology direct connect mental processes to biological mechanisms. Brain imaging technologies like fMRI and EEG provide objective measurements of neural activity associate with psychological phenomena. This biological foundation strengthens psychology’s classification as a science.
Quantitative approaches
Psychological assessment frequently involves standardize testing, psychometrics, and statistical analysis. Intelligence tests, personality inventories, and behavioral measures generate numerical data that canbe analyzede mathematically. This quantitative approach align psychology with other scientific disciplines that rely on measurement and statistical inference.
The application of computational modeling in psychology far demonstrate its scientific character. Researchers create mathematical models of cognitive processes, neural networks, and behavioral patterns. These models generate testable predictions about human functioning, follow the pattern of theoretical and applied sciences.
The artistic elements of psychology
Interpretive understanding
Despite its scientific methodology, psychology besides incorporate interpretive approaches more common to the humanities. Clinical psychology and psychotherapy oftentimes involve narrative understanding, empathetic connection, and meaning make processes that resist strictly quantitative analysis. The therapeutic relationship rely on interpersonal skills and interpretive judgment that resemble artistic practice.
Qualitative research methods in psychology, include phenomenological analysis, narrative inquiry, and case studies, emphasize subjective experience and contextual understanding. These approaches share methodological features with disciplines in the humanities like literature, philosophy, and cultural studies.
Cultural and social dimensions
Cross-cultural psychology and social psychology examine how human behavior vary across different cultural contexts and social environments. These subfields oftentimes require interpretive sensitivity to cultural meanings, social norms, and historical contexts. This cultural dimension connects psychology to anthropology, sociology, and other social sciences that bridge arts and sciences.
The application of psychological insights in fields like literature, art, and media analysis demonstrate psychology’s relevance to artistic and humanistic endeavors. Psychological perspectives enrich our understanding of creative works, while artistic expressions provide valuable insights into psychological phenomena.
Bachelor of arts vs. Bachelor of science in psychology
Curriculum differences
The distinction between a BA and BS in psychology reflect the field’s dual nature. A bachelor of arts in psychology typically include:

Source: studylib.net
- Greater emphasis on liberal arts courses
- More electives in humanities and social sciences
- Focus on qualitative research methods
- Courses in abnormal psychology, personality, and social psychology
- Less intensive mathematics and statistics requirements
In contrast, a bachelor of science in psychology mostly feature:
- Stronger emphasis on research methodology
- More rigorous statistics and mathematics requirements
- Laboratory courses and experimental design
- Greater focus on biological bases of behavior
- Additional natural science requirements
Institutional classification
The classification of psychology programs vary across institutions. Some universities house psychology departments within their college of arts and sciences, reflect its interdisciplinary nature. Others place psychology within specific schools like social sciences, natural sciences, or evening separate colleges of psychology.
This institutional variation reflect ongoing debates about psychology’s disciplinary identity. The American psychological association recognize psychology as a stem (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics )discipline, though this classification reremainsontest in some academic circles.
Career implications
Ba in psychology career paths
Graduates with a BA in psychology frequently pursue careers that leverage their understanding of human behavior in social contexts:
- Human resources and personnel management
- Social services and community support
- Marketing and consumer behavior analysis
- Educational support services
- Counseling (with additional graduate education )
The BA path may be especially suitable for students interested in apply psychological principles in human services, business environments, or educational settings. The broader liberal arts foundation provide versatility for various career paths.
BS in psychology career paths
Students who complete a BS in psychology may be advantageously positioned for careers with stronger scientific components:
- Research assistantships in laboratories
- Data analysis and behavioral statistics
- Neuropsychological testing
- Health services coordination
- Graduate programs in experimental psychology, neuroscience, or clinical psychology
The BS path typically provides stronger preparation for research orient graduate programs and careers require quantitative skills. The additional scientific training may be advantageous for students plan careers in research or clinical settings.
Graduate education considerations
For students consider graduate education in psychology, the choice between BA and BS programs carry implications for future specialization. Clinical psychology programs frequently accept students from both BA and BS backgrounds, though research intensive programs may prefer candidates with stronger scientific preparation.
Doctoral programs in experimental psychology, cognitive science, and neuroscience typically favor applicants with substantial research experience and quantitative skills. Yet, counsel psychology, school psychology, and some clinical programs value the broader preparation provide by a BA curriculum.

Source: psychologychoices.blogspot.com
Integrative perspectives
Psychology as a hybrid discipline
Instead, than force psychology into either the arts or sciences category, many scholars recognize it as a hybrid discipline that draw strength from both traditions. This integrative perspectiveacknowledgese psychology’s methodological diversity as a strength quite than a weakness.
The scientist practitioner model in clinical psychology explicitly combines scientific research with humanistic practice. Clinical psychologists are train to apply scientific findings while maintain sensitivity to individual differences and contextual factors that require interpretive understanding.
Contemporary trends
Current trends in psychology education progressively emphasize interdisciplinary approaches that transcend traditional arts science boundaries. Programs in cognitive science combine psychology with linguistics, philosophy, computer science, and neuroscience. Likewise, behavioral economics integrate psychological insights with economic theory.
The emergence of mixed methods research designs reflect psychologies grow methodological sophistication. These approaches combine quantitative measurement with qualitative understanding, acknowledge that complex human phenomena require multiple investigative lenses.
Make your decision
Personal factors to consider
When decide between a BA and BS in psychology, consider these personal factors:
- Your comfort level with mathematics and statistics
- Interest in biological aspects of behavior versus social and cultural dimensions
- Preference for experimental research versus apply human services
- Long term career and educational goals
- Desire for breadth versus depth in your undergraduate education
Many students choose base on their strengths and interests quite than abstract disciplinary classifications. Your learn style and career aspirations should guide this decision more than debates about whether psychology is essentially an art or science.
Program specific research
Before make your decision, research specific programs at your institutions of interest. Some universities offer most identical BA and BS curricula with minor differences, while others maintain substantial distinctions between these degree paths.
Speak with academic advisors, current students, and recent graduates can provide valuable insights beyond formal program descriptions. Faculty members can frequently clarify how their specific department approach the arts science balance in psychology education.
Conclusion
Psychology defy simple classification as either art or science. Rather, it draws strength from both traditions, combine empirical research methods with interpretive understanding of human experience.Whetherr psychology belong to the arts or sciences reflect ongoing tensions within the discipline about its fundamental identity and methodological approaches.
The choice between a bachelor of arts or bachelor of science in psychology allow students to emphasize different aspects of this multifaceted discipline. Instead, than view this as a binary choice between art and science, consider it an opportunity to customize your education to align with your interests, strengths, and career goals.
Finally, psychology’s position at the intersection of arts and sciences represent not a weakness but a unique strength. This disciplinary flexibility allow psychology to address human behavior and mental processes from multiple perspectives, contribute to our understanding of the virtually complex phenomenon in the know universe — the human mind.
MORE FROM nicoupon.com