Transforming Science Education: Harnessing Virtual Reality for Scientific Visualization

Photo by Hammer & Tusk on Unsplash
Introduction: A New Era for Science Education
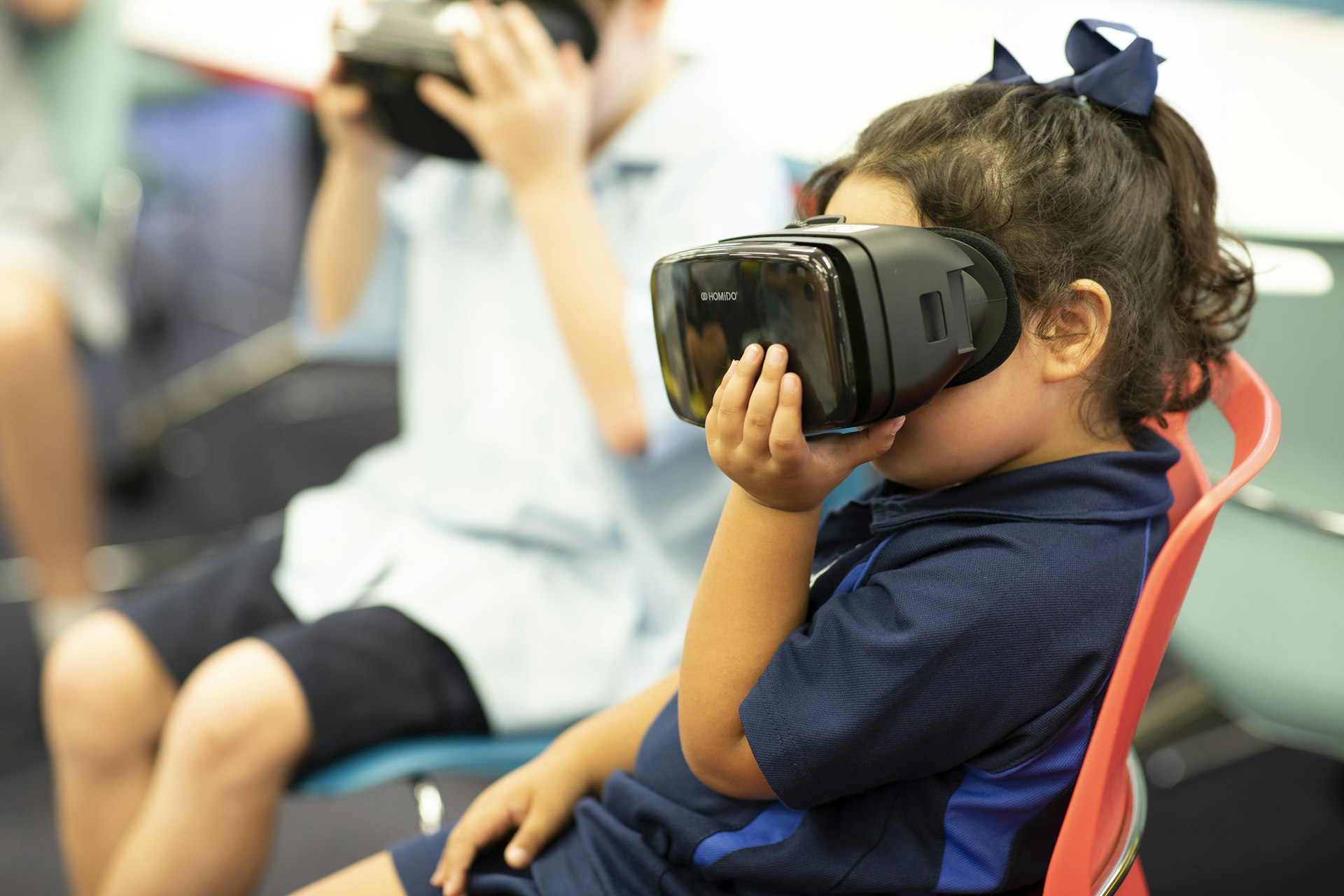
Virtual reality (VR) is rapidly changing the landscape of science education. No longer limited to textbook illustrations or static images, students and educators can now step inside complex scientific phenomena, explore the human body at the molecular level, or travel through outer space-all within a classroom setting. The integration of VR for scientific visualization is making science more accessible, interactive, and memorable for learners of all ages [1] .
The Power of Visualization: Why VR Works in Science Learning
One of the most significant challenges in science education is helping students grasp abstract or complex concepts. VR addresses this by providing immersive, three-dimensional environments where students can interact directly with scientific models. For example, instead of simply reading about the structure of DNA, learners can manipulate a virtual double helix, observing how its components interact in real time [1] . This hands-on approach leads to better retention, increased motivation, and deeper conceptual understanding [4] .
Research supports these benefits. In engineering education, immersive VR simulations have led to significant improvements in test scores, with some studies showing a 20% increase in performance when students used VR before engaging in physical labs [2] . In biology, mixed reality classrooms have produced higher learning outcomes and improved information retention by nearly 9% compared to traditional teaching methods [3] .
Key Benefits: Engaging, Inclusive, and Effective
1. Enhanced Engagement and Motivation: Students find science lessons more engaging when they can “walk through” the circulatory system or observe planetary orbits from inside a virtual solar system [1] . This interactivity fosters curiosity, encourages exploration, and can transform even reluctant learners into active participants.

Photo by stem.T4L on Unsplash
2. Improved Learning Outcomes: The immersive nature of VR enables students to practice experiments, visualize processes, and repeat complex tasks as often as needed. Notably, VR has been shown to double female STEM students’ test score improvements in some studies, suggesting that VR can also help bridge gender gaps in science education [2] .
3. Accessibility and Inclusivity: VR provides opportunities for students who may not have access to well-equipped laboratories or field trips. It creates an inclusive environment where all learners can participate, regardless of physical ability or location [5] .
4. Promoting Creative and Critical Thinking: Beyond passive observation, current best practices emphasize using VR as a tool for creation. Students can build their own models, program virtual experiments, and test hypotheses in a risk-free environment. This approach deepens understanding and mirrors authentic scientific inquiry [4] .
Real-World Examples: VR in Action
Consider a high school biology class using VR to explore cell division. Students don headsets and witness mitosis at the microscopic level, identifying each stage as it unfolds around them. In another example, chemistry students safely simulate mixing chemicals to observe reactions that would be too dangerous in a real lab [1] .
Some VR platforms enable students to build and test bridges in virtual environments, experimenting with different materials and designs before seeing the results in a simulated “stress test.” This not only reinforces physics concepts but also fosters creativity and problem-solving skills [4] .
Implementation: How to Bring VR into Your Science Classroom
Integrating VR for scientific visualization can be achieved through several steps:
1. Assess Your Needs and Goals: Start by identifying the scientific concepts or skills you wish to enhance with VR. Consider whether your primary goal is visualization, experimentation, or student creation.
2. Choose Appropriate VR Tools: There are many VR platforms and apps specifically designed for education. Seek out tools that align with your curriculum and provide age-appropriate experiences. Many reputable organizations and educational technology providers offer VR science content. For the most current options, you can search for “top VR science education platforms” or consult with your local school district’s technology coordinator.
3. Address Hardware and Accessibility: Determine what VR equipment is needed. While some VR experiences require advanced headsets, many platforms offer browser-based or mobile-compatible options that are more affordable. If purchasing equipment is a barrier, you may be able to access VR resources through local libraries, educational consortia, or grant-funded programs. Contact your district’s educational technology department or search for “educational VR grants” for opportunities.
4. Teacher Training and Support: Effective integration requires teacher training. Many educational technology companies offer professional development workshops. If these are not available locally, you can search for “VR in education professional development” to find reputable online courses or webinars.
5. Start Small and Scale Up: Begin with pilot lessons or modules. Gather feedback from students and adjust your approach as needed. Over time, expand VR integration across more topics and grade levels for maximum impact.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
Despite its benefits, VR adoption in science education may face several challenges:
Cost: High-end VR headsets can be expensive. However, many educational VR platforms now support affordable options like mobile VR viewers or browser-based simulations. Schools may also partner with community organizations or apply for grants to offset costs.
Technical Support: Successful implementation depends on reliable hardware and software. Establish a support system by training staff, designating a technology coordinator, and maintaining regular equipment checks.
Accessibility: Ensure all students, including those with disabilities, can participate. Many VR providers now offer adjustable settings and alternative input methods. Consult with your school’s special education department for best practices in inclusive technology use.
Alternative Pathways and Additional Resources
Not every school can immediately invest in a full suite of VR equipment. Alternative approaches include:
- Desktop Simulations: Many scientific visualization tools are available as desktop applications, providing interactive 3D models without the need for headsets.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR apps on smartphones or tablets can overlay scientific models onto real-world environments, offering a lower-cost entry point.
- Community Partnerships: Collaborate with local universities, science centers, or museums, many of which offer VR-based outreach programs.
For up-to-date guidance on VR tools and educator resources, you can:
- Search official education technology websites like the International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE).
- Consult your state’s department of education for approved digital learning resources.
- Contact your local library or educational service agency to inquire about available VR kits or lending programs.
Conclusion: The Future of Scientific Visualization in Education
Virtual reality is ushering in a new era of scientific visualization in education, making abstract concepts tangible and inspiring the next generation of scientists, engineers, and innovators. Whether through immersive exploration, hands-on experimentation, or student-driven creation, VR provides diverse pathways for deeper learning. By leveraging the strategies and resources outlined above, educators, administrators, and students can begin to access and benefit from this transformative technology.
References
- [1] Teachers Tech (2024). Beyond the Textbook: Immersive Learning with VR in Science.
- [2] ENGAGE XR (2024). Benefits of Virtual Reality for Education.
- [3] American University School of Education (2019). Virtual Reality in Education: Benefits, Tools, and Resources.
- [4] Hello World CS (2025). The Benefits of Virtual Reality in Education.
- [5] National Institutes of Health (2023). An Examination of the Effects of Virtual Reality Training on Spatial Ability.
MORE FROM nicoupon.com